Propane Safety in the Workplace
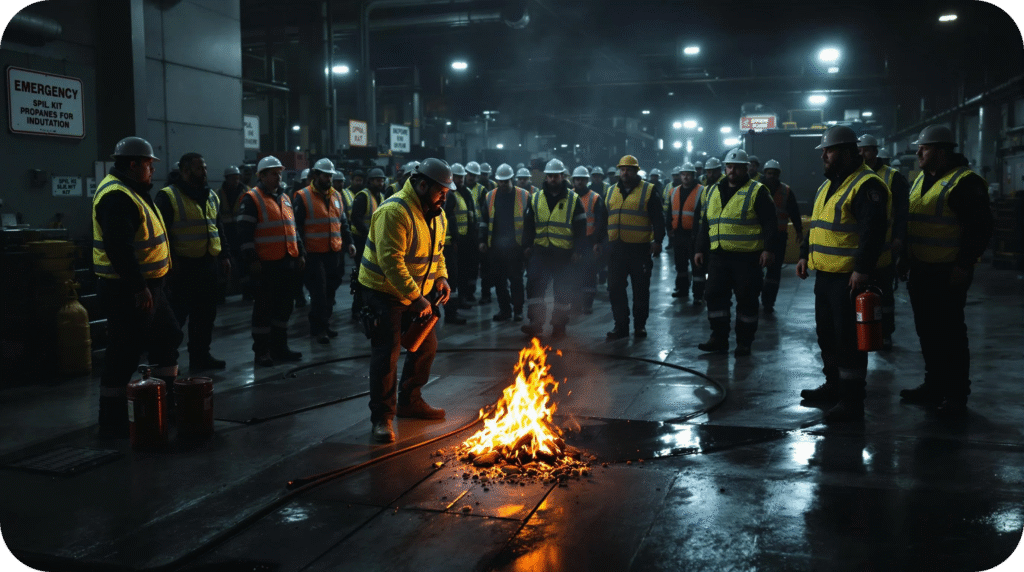
Propane is versatile and efficient but can be dangerous if mishandled. Learn essential safety tips for transport, storage, handling, and emergencies.
ProAct – Shawn Galloway on Safety Excellence: Why Culture, Strategy, and Ownership Matter Most

In this episode, global safety strategist Shawn Galloway breaks down what it really takes to achieve safety excellence.
Humor at Work – Work Shouldn’t Suck: Mike Kerr on Humor, Culture, and Why Safety Starts with Fun

Luca Filippo shares his journey through aviation and biology, plus what it taught him about safety culture.
Fire Drills: How to Turn Routine Practice into Real-World Readiness

Conducting regular fire drills is more than a formality—it’s essential for building confidence, reinforcing roles, and ensuring workplace teams respond swiftly during real emergencies.
Lock Out Tag Out: The Safety Standard Every Team Should Master

LOTO compliance protects workers in Canadian industries by requiring equipment to be locked and tagged during repair or inspection activities.
Why Incident Reports Fuel Safety Culture

Understand how timely incident reporting improves workplace safety, supports compliance, and drives meaningful safety improvements across Canadian industries.
University of Alberta – The Universal Language of Risk: Lucca Filippo on Safety Lessons Learned Across Airspace and Labs

Luca Filippo shares his journey through aviation and biology, plus what it taught him about safety culture.
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS): A Proactive Approach to Workplace Safety

Want a safer workplace that actually sticks? Behavior-Based Safety focuses on everyday choices and teamwork. When people observe, speak up, and support one another, safety becomes something everyone owns—and that’s when the real change begins.
SAFEmap International – The Risk Paradox: Corrie Pitzer on Paralysis By Safety

Dr. Tom Krause shares lessons from decades in safety leadership, covering behavior-based safety, decision analysis, and why real change goes beyond blaming employees.
Solution Folder – Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace with Mehmet Baha

From Fulbright scholar to Facebook Europe’s early days to bestselling author, Mehmet Baha’s journey is anything but ordinary.




























