Ensuring the safety of employees is a top priority for any business, regardless of the industry. From construction sites to corporate offices, maintaining a safe work environment is essential for protecting your workforce and minimizing risks. However, safety training is often seen as an expense rather than an investment, leading many business owners to wonder if it’s truly cost-effective in the long run. This question becomes even more pressing when deciding between purchasing single safety training courses or opting for subscription-based packages.
In this blog, we’ll dive into the financial implications of both options. We’ll explore the hidden costs of workplace accidents, analyze turnover costs across various industries, and introduce a practical formula to help you calculate the long-term costs of safety training. By the end, you’ll have a clearer picture of whether safety training course subscriptions can offer your business significant savings and other benefits over time.
The True Cost of Workplace Accidents
Workplace accidents carry a heavy financial burden that extends far beyond the immediate medical costs. When an employee is injured on the job, businesses face a myriad of direct and indirect expenses that can quickly add up. Here’s a closer look at these costs:
Direct Costs
- Medical Expenses: These include emergency treatment, hospital stays, surgeries, medications, and rehabilitation services. Even minor injuries can result in substantial medical bills.
- Workers’ Compensation: Employers are required to cover workers’ compensation, which pays for medical treatment and lost wages for injured employees. Premiums for this insurance can rise significantly after a workplace accident.
Indirect Costs
- Lost Productivity: When an employee is injured, their absence can disrupt workflows, delay projects, and reduce overall productivity. The time taken to find a temporary replacement or redistribute tasks among existing employees also affects efficiency.
- Legal Fees and Fines: If the accident results in legal action, businesses may face hefty legal fees and potential fines for non-compliance with safety regulations. These costs can escalate quickly and strain financial resources.
- Impact on Employee Morale and Turnover: Workplace accidents can lead to a decline in employee morale, as workers may feel unsafe or undervalued. This can increase turnover rates, leading to further costs associated with hiring and training new employees.
The financial impact of workplace accidents underscores the importance of comprehensive safety training. By equipping employees with the knowledge and skills to avoid hazards, businesses can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents, thereby mitigating these costs. Investing in safety training is not just about compliance—it’s about fostering a safer, more productive work environment that benefits everyone in the long run.

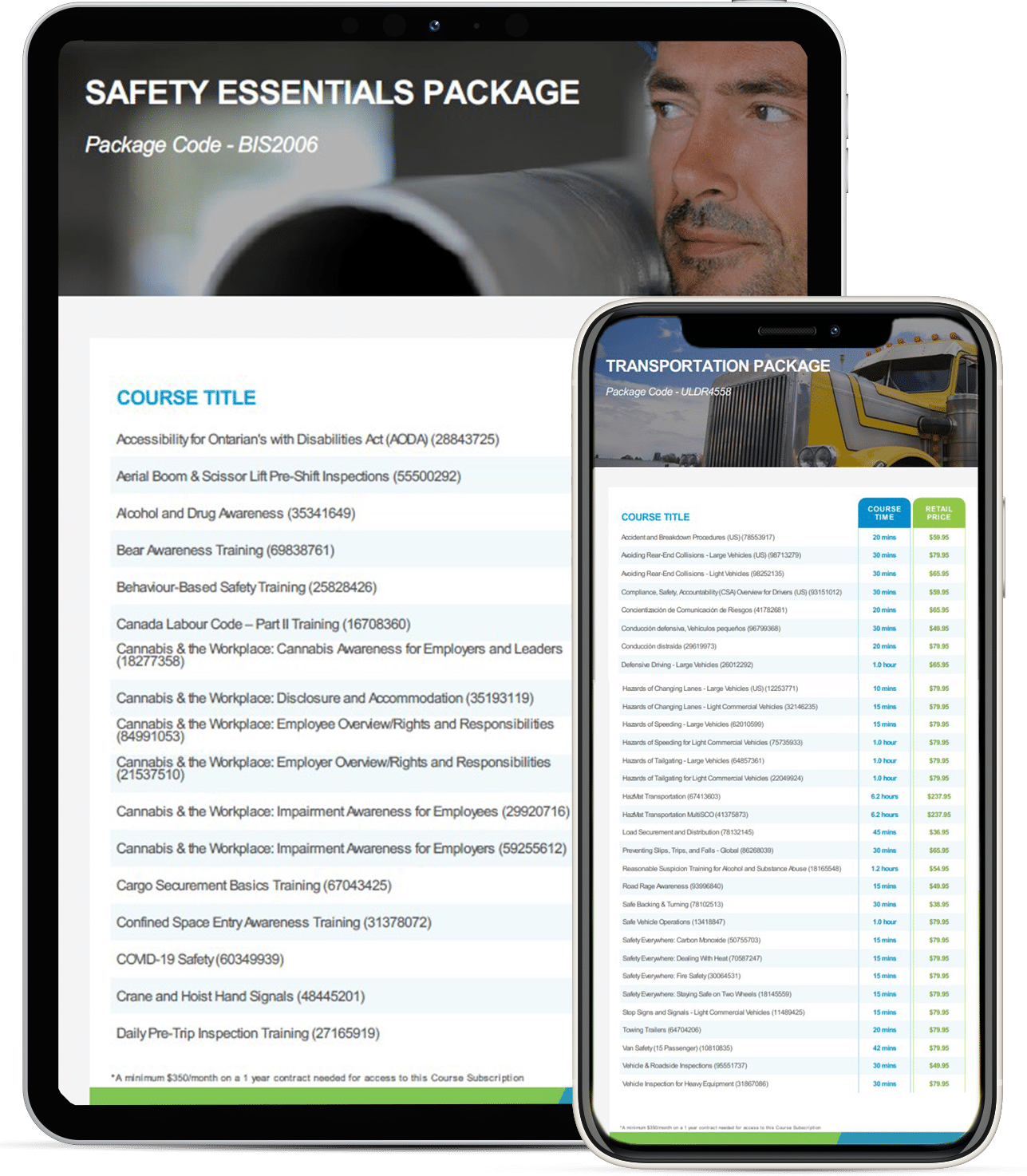
Cost Comparison: Single Courses vs. Subscription Packages
Single Safety Training Courses
Pros:- Specific Focus: Single courses allow you to target specific training needs, addressing particular hazards or compliance requirements relevant to your business.
- One-Time Payment: With a single payment, you gain access to the training material, which can be reused for new hires or refresher courses.
- Limited Scope: Single courses often cover specific topics, which means you might need to purchase multiple courses to cover all necessary training areas.
- Higher Costs Over Time: As your training needs evolve, purchasing individual courses can become expensive, especially if you have a large workforce or high turnover.
Safety Training Course Subscriptions
Pros:- Comprehensive Access: Subscriptions provide access to a wide range of training courses, covering various safety topics and compliance requirements.
- Continuous Updates: Training materials are regularly updated to reflect the latest regulations and industry best practices, ensuring your employees always have access to current information.
- Cost-Effective: For businesses with ongoing training needs, subscriptions can be more cost-effective over time, offering significant savings compared to purchasing individual courses.
- Recurring Payment: Subscriptions require an annual or monthly fee, which may be a consideration for businesses with tight budgets.
- Potential Underuse: If not all courses are utilized, the full value of the subscription might not be realized.
Formula for Calculating Long-Term Costs
To determine which option is more cost-effective for your business, it’s essential to calculate the long-term costs of both single courses and subscription packages. Here’s a formula to help you with this comparison:Step 1: Calculate Turnover Costs
Turnover costs can vary significantly by industry, but here’s a general approach to estimate these costs:- Total Turnover Cost = Number of Employees x Turnover Rate x Turnover Cost per Employee
- Number of Employees: 100
- Turnover Rate: 10% (0.10)
- Turnover Cost per Employee: $20,000
Step 2: Calculate Training Costs for Single Courses
- Training Costs for Single Courses = Number of Courses x Cost per Course
- Number of Courses: 5
- Cost per Course: $60
Step 3: Calculate Training Costs for Subscriptions
- Training Costs for Subscriptions = Annual Subscription Cost x Number of Years
- Annual Subscription Cost: $20 per user/year
- Number of Years: 5
Step 4: Compare Long-Term Costs
Combine the turnover costs and training costs to get the total cost for each option over a specified period. Total Cost for Single Courses (5 Years):- Total Cost = Turnover Cost + Training Costs for Single Courses
- Total Cost = $200,000 + (5 x $30,000) = $200,000 + $30,000 = $230,000
- Total Cost = Turnover Cost + Training Costs for Subscriptions
- Total Cost = $200,000 + $10,000 = $210,000
Understanding the True Turnover Costs of Training Per Industry
Turnover costs can vary significantly depending on the industry, the complexity of the job roles, and the level of expertise required. Understanding these costs is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about their safety training investments. Let’s explore how turnover costs manifest in different industries and the impact they have on overall expenses.
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing industry, the turnover costs are particularly high due to the specialized skills required and the potential impact on production. Here’s a breakdown of the turnover costs in manufacturing:
- Recruiting and Hiring Costs: Finding and hiring skilled workers in manufacturing can be expensive, often involving recruitment agencies, advertising, and extensive interview processes.
- Training Costs: New hires need to be trained on specific machinery, safety protocols, and production processes. This training period can vary from a few weeks to several months, during which the new employee is not fully productive.
- Lost Productivity: Until new hires reach full productivity, existing employees may need to work overtime or the company may have to hire temporary workers, increasing costs.
- Quality and Safety Issues: Inexperienced workers are more prone to making mistakes, which can lead to product defects, rework, and increased safety risks.
Average Turnover Cost in Manufacturing: Studies estimate that the average turnover cost per employee in manufacturing can range from 16% to 20% of the annual salary. For a mid-level worker earning $50,000 per year, this translates to $8,000 to $10,000.
Construction
The construction industry faces high turnover costs due to the physically demanding nature of the work and the need for compliance with strict safety regulations. Key turnover cost factors include:
- Recruiting and Hiring Costs: Similar to manufacturing, recruiting skilled construction workers involves significant expenses in advertising and recruitment services.
- Training Costs: New employees must be trained on site-specific safety protocols, equipment operation, and construction techniques, which can be time-consuming and costly.
- Lost Productivity: The learning curve for new hires can slow down project timelines, requiring additional oversight and potentially causing delays.
- Safety Risks: Construction sites are inherently hazardous, and inexperienced workers may increase the risk of accidents and injuries, leading to further costs.
Average Turnover Cost in Construction: Turnover costs in the construction industry are estimated to be around 20% to 25% of an employee’s annual salary. For a construction worker earning $45,000 per year, this equates to $9,000 to $11,250.
Healthcare
Healthcare turnover costs are substantial due to the high level of specialization and the critical nature of the work. Factors contributing to these costs include:
- Recruiting and Hiring Costs: Hiring healthcare professionals often requires extensive background checks, credential verification, and possibly relocation expenses.
- Training Costs: New hires need to undergo rigorous training to familiarize themselves with hospital protocols, electronic health records systems, and patient care standards.
- Lost Productivity: The onboarding period can be lengthy, and during this time, the workload on existing staff increases, potentially leading to burnout and further turnover.
- Patient Safety and Quality of Care: High turnover can impact patient care quality and safety, as continuity of care is disrupted and experienced staff are stretched thin.
Average Turnover Cost in Healthcare: Turnover costs in healthcare can be as high as 50% to 100% of an employee’s annual salary. For a registered nurse earning $70,000 per year, this means costs ranging from $35,000 to $70,000.
Retail
The retail industry experiences high turnover rates due to the entry-level nature of many positions and seasonal fluctuations in staffing needs. Key turnover cost components include:
- Recruiting and Hiring Costs: While recruiting costs are generally lower in retail, they can add up due to the high volume of hires required.
- Training Costs: Training new employees in customer service, point-of-sale systems, and inventory management is necessary, though usually shorter than in other industries.
- Lost Productivity: New hires take time to become efficient, and during this period, customer service and sales performance may be impacted.
- Impact on Customer Satisfaction: Frequent turnover can affect customer satisfaction and loyalty, as customers often prefer familiar and knowledgeable staff.
Average Turnover Cost in Retail: Turnover costs in retail are estimated to be around 16% of an employee’s annual salary. For a retail worker earning $25,000 per year, this translates to $4,000.

Benefits Beyond Cost Savings
Continuous Access to Updated Training Materials
With subscription packages, you gain continuous access to a broad range of training courses that are regularly updated to reflect the latest industry standards and regulatory requirements. This ensures your employees always receive the most current and relevant training, helping to maintain high safety standards and compliance.Easier Tracking of Employee Progress and Compliance
Subscription services often come with integrated tracking and reporting tools. These tools allow you to monitor employee progress, track completion rates, and ensure compliance with mandatory training requirements. This not only simplifies administrative tasks but also provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of your training programs.Flexibility in Training Schedules
Subscriptions offer the flexibility to train employees at their own pace and on their own schedules. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses with shift workers or remote teams, ensuring that all employees have equal access to training without disrupting daily operations.Enhanced Employee Engagement and Knowledge Retention
Regular, ongoing training can lead to better knowledge retention and higher employee engagement. Subscriptions often include interactive and varied content formats such as videos, quizzes, and simulations, which can make learning more engaging and effective. Engaged employees are more likely to apply what they learn in their daily tasks, contributing to a safer work environment.Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Choosing between single safety training courses and subscription packages depends on several factors specific to your business. Here are some tips to help you make the right decision:Assess the Size of Your Workforce and Turnover Rates
Consider the number of employees who need training and your industry’s turnover rates. Businesses with a large workforce or high turnover may benefit more from the cost savings and comprehensive access provided by subscription packages.Consider Industry-Specific Safety Training Needs
Different industries have unique safety training requirements. Evaluate whether your industry demands frequent updates and a wide range of training topics, which may make a subscription more advantageous.Evaluate Budget Constraints and Long-Term Goals
Analyze your budget and long-term goals for employee safety and compliance. While subscriptions may require a higher upfront cost, they often provide greater value and savings over time. Align your choice with your financial capacity and strategic objectives.Conclusion
Investing in safety training is crucial for protecting your employees and minimizing risks in the workplace. While single courses may seem cheaper upfront, safety training course subscriptions often offer significant cost savings and additional benefits over the long run. By providing continuous access to updated training materials, simplifying compliance tracking, offering flexible training schedules, and enhancing employee engagement, subscriptions can be a more effective and economical solution for many businesses.
To determine the best option for your organization, consider your workforce size, turnover rates, industry-specific needs, and long-term goals. Use the provided formula to calculate and compare the long-term costs of single courses versus subscriptions. Ultimately, the right investment in safety training can lead to a safer, more productive work environment and substantial financial savings.
Ready to Switch to Training Course Subscriptions?
Ready to explore the benefits of safety training course subscriptions for your business? Visit BIS Safety Software to discover our comprehensive training solutions. Our team is here to help you choose the best subscription plan tailored to your needs. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and take the first step towards a safer workplace!
Related Articles
- All Posts
- 360 Immersive
- 360immersive
- accident prevention
- Alberta safety courses
- Allan James Moore
- asking for help
- avoidable injuries
- awareness
- back strain
- BambooHR integration
- biometric sensors
- BIS Podcast
- BIS Safety Software
- black holes
- Brave Leadership
- burnout
- Canadian safety history
- carbon monoxide
- CCOHS
- chemical
- chemical vapors
- chronic injuries
- chronic pain
- Coming Soon
- community safety programs
- Compliance
- compliance courses
- compliance tools
- compliance vs protection
- Construction advocacy
- Construction education
- Construction industry
- construction safety training
- continuous safety improvement
- crane
- customized training
- daily trip inspection
- Danny Sellers
- data-driven safety
- digital forms
- Dr. Joanna Pagonis
- driver file management
- driver training
- early intervention
- EHS
- Einstein
- electrical safety
- emergency preparedness
- emergency response
- emergency supplies
- emotional training
- employee health
- employee safety
- employee training
- ergonomic risks
- ergonomics
- evidence collection
- exoskeletons
- fall protection
- field safety
- field safety services
- fire prevention
- first aid kit
- first week on the job
- first workplace injury
- fleet management
- frontline safety
- gravitational waves
- hand injuries
- hands-on training
- hazard communication
- hazard prevention
- hazard recognition
- Health & Safety Podcast
- hearing loss prevention
- heavy equipment safety
- hidden workplace hazards
- high voltage systems
- HR automation
- HR software
- human-centered safety
- humor in safety
- immersive learning
- Imposter Syndrome
- incident data
- incident investigation
- incident reporting
- industrial safety
- injury consequences
- injury prevention
- injury prevention tips
- injury recovery
- injury reporting
- injury response
- injury response plan
- internal audits
- invisible dangers
- Jennifer Lastra
- job site hazards
- job site risks
- job site safety
- Jody Young
- KBR Safety Training
- labor movement
- ladder safety
- Leadership
- leadership accountability
- leadership and empathy
- learning from incidents
- lifting techniques
- LIGO
- LMS
- lockout tagout
- lone workers
- mental health at work
- MI Safety
- minor injuries
- new workers
- no-blame investigations
- noise exposure
- Northern BC
- NRCA
- NSC Standard 13
- occupational fatigue
- occupational hazards
- occupational health
- occupational safety
- OHSA
- oil and gas safety
- onboarding safety
- Online safety training
- organizational safety
- OSHA compliance
- OSHA standards
- overhead crane courses
- pain awareness
- personal protective equipment
- physics careers
- pipeline safety
- podcast
- post-accident review
- post-incident protocol
- PPE
- PPE enforcement
- PPE improvement
- pre-trip inspection
- pretrip inspection
- proactive safety measures.
- Professional development
- psychological hazards
- psychological safety
- repetitive motion injuries
- respirator safety
- risk management
- risk reduction
- road safety
- Robin Postnikoff
- root cause analysis
- routine task risks
- safe work habits
- safety
- safety accountability
- safety advice
- safety article
- safety awareness
- safety best practices
- safety communication
- safety compliance
- Safety Conversations
- safety culture
- safety engagement
- safety follow-up
- safety gear
- safety habits
- safety innovation
- safety insights
- safety inspection
- Safety Leaders
- safety leadership
- safety legislation
- safety lessons
- safety management
- safety management system
- safety metrics
- safety motivation.
- safety myths
- safety podcast
- safety procedure updates
- safety review process
- safety shortcuts
- Safety Spotlight
- safety systems
- safety technology
- safety theater
- safety tips
- safety training
- safety transparency
- silent dangers
- silica dust
- Sinogap Solutions
- slow-building hazards
- smart helmets
- space science
- supervisor training
- team communication
- teamwork
- Total Recordable Injury Formula
- tough guy mentality
- toxic air
- training
- training courses
- training matrix
- training record management
- transportation
- Trust and Accountability
- unseen workplace threats
- vehicle safety
- veteran advice
- Virtual Reality
- VR safety training
- VR Technology
- wearable technology
- WHMIS
- witness statements
- women in leadership
- work-alone training
- work-related injuries
- worker accountability
- worker advocacy
- worker fatigue
- worker protection
- worker safety
- worker safety habits
- worker trust
- workers' rights
- workforce management
- workforce training
- workplace accidents
- workplace air quality
- workplace best practices
- workplace certification
- Workplace Culture
- workplace hazards
- workplace health
- workplace incident response
- workplace injuries
- workplace injury prevention
- workplace mindset
- workplace risk factors
- workplace risk management
- Workplace safety
- workplace safety culture
- workplace safety rules
- workplace safety tips
- workplace safety training
- workplace stress
- workplace tiredness
- workplace wellness
- WSPS

Too many workers risk injury by refusing help to appear tough. This article explains how asking for help and supporting...

Canada’s safety standards weren’t handed down—they were hard-won. This article explores the rise of workplace safety from the early industrial...

Workplace safety cultures fall into three categories: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Some organizations set the gold standard...


























