BIS Safety Software
Online Course Subscriptions
Sign-up for a Subscription for Unlimited Access to All Included Courses
Choose from the Ten Course Subscriptions Packages
*All course subscriptions require a 1-year contract. A $500 fee is used to set up your custom portal. Pricing is subject to change.
Safety Basics
Subscription
Access 50 online courses
Number of users
Monthly price/user
50-499
$1.50
500-999
$1.40
1000-1499
$1.30
1500-2499
$1.20
2500-4999
$1.10
Safety Essentials
Subscription
Access 100+ online courses
Number of users
Monthly price/user
25-499
$3.50
500-999
$3.28
1000-1499
$2.98
1500-2499
$2.83
2500-4999
$2.60
Regulatory Compliance Subscription
Access 165+ online courses
Number of users
Monthly price/user
50-99
$6.00
100-249
$4.50
250-499
$3.75
500-999
$3.30
1000-2499
$3.00
Construction
Subscription
Access 75+ online courses
Number of users
Monthly price/user
50-499
$12.66
500-999
$9.68
1000-2499
$6.70
2500-4999
$5.22
5000+
$3.72
Driver & Hazmat
Subscription
Access 140+ online courses
Number of users
Monthly price/user
100-249
$7.04
250-499
$4.00
500-999
$3.12
1000-1999
$2.60
2000-2999
$2.12
Transportation
Subscription
Access 40+ online courses
Number of users
Monthly price/user
50-499
$7.46
500-999
$6.70
1000-2499
$5.96
2500-4999
$5.22
5000+
$4.48
Complete Safety
Subscription
Access 200+ online courses
Number of users
Monthly price/user
100-249
$9.62
250-499
$5.36
500-999
$4.18
1000-1999
$3.42
2000-2999
$3.06
Safety & Awareness
Subscription
Access 120+ online courses
Number of users
Monthly price/user
100-499
$7.46
500-999
$6.20
1000+
$4.94
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Industrial Workplace
Subscription
Access 375+ online courses
Number of users
Monthly price/user
50-499
$20.12
500-999
$16.40
1000-2499
$12.66
2500-4999
$10.44
5000+
$8.20
Workplace Safety
& HR Subscription
Access 170+ online courses
Number of users
Monthly price/user
100-249
$7.04
250-499
$4.00
500-999
$3.12
1000-1999
$2.60
2000-2999
$2.12
BIS Safety Software
Every Course Subscription Includes:
Subscriptions Also Include additional benefits and features at no extra cost.
All in a convenient, user-friendly platform!
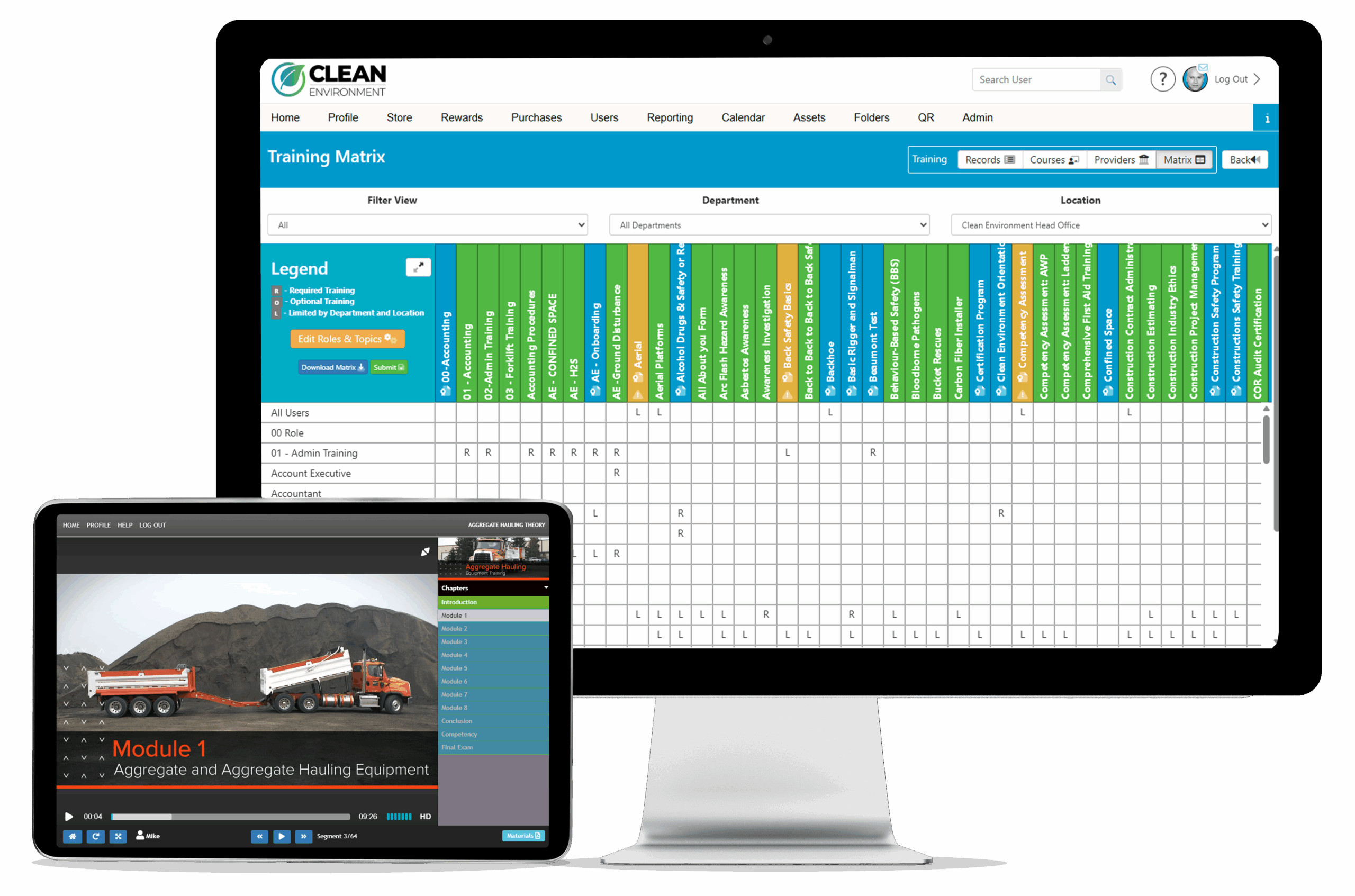
The Training Matrix
As a part of the course package, you have access to an enterprise-level Training Matrix, which includes:
- The ability to automate employee training assignments by role and location
- Summary reports to see training gaps
- User management and permission controls
- An integrated eCommerce store, and course permissions
- Create custom certification programs with automatic assignments
Utilize your own robust training matrix to reduce the administrative work associated with your employee training program!
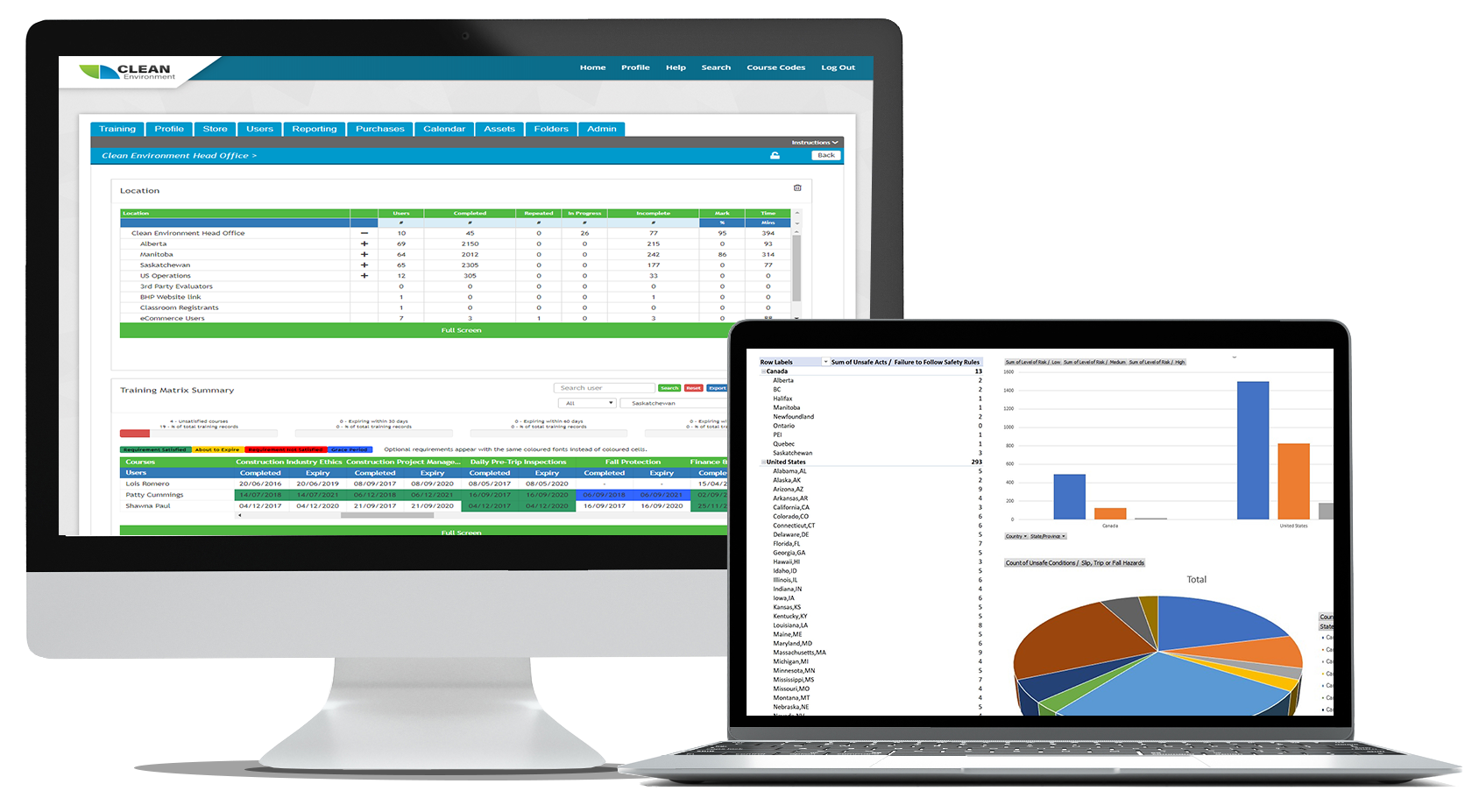
Automated Reporting
Reporting and Automatic Notifications
*All course subscriptions require a 1-year contract.
A $500 fee is used to set up your custom portal. Pricing is subject to change.
- View online report dashboards and receive automated notifications for topics such as:
- Training gaps and expiring certificates
- Course completions by employee
- Location-specific reports for each office and job site
- And much more
- You can also download all of your reporting data into Excel-compatible formats so that you can continue reviewing the information even if you are offline. You can also utilize Excel reports to create your own custom data visualizations.
BIS Safety Software
Subscriptions Also Include:
Reporting and Automatic Notifications
Your employees need great training for both their skills and their safety. One of the best ways to show proof of training is with a certificate of completion. Each online course in the BIStrainer system provides a certificate to make it easy to confirm whether your employees have the training they need.
Training certificates can be displayed on your phone or tablet and verification of completed training can be conducted quickly every time your employee enters a new job site.

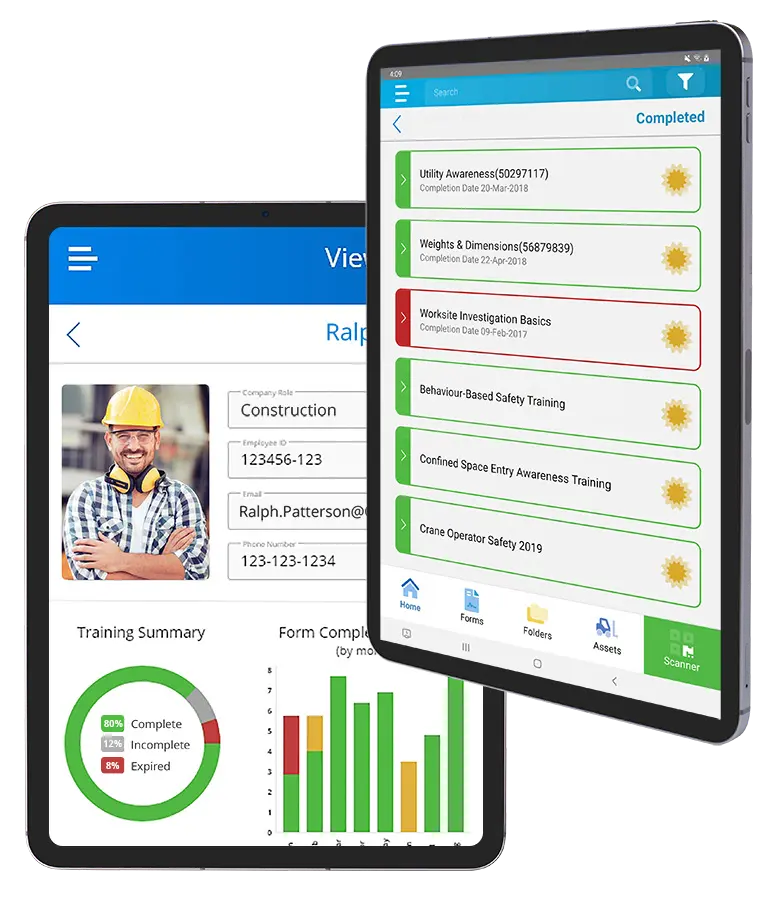
Mobile Access to Training and Certificates
Get Started!
Tired of using energy on things that can be automated like exam evaluations? Our secure online evaluation tool handles exams, assessments, and surveys for you.




























